- Suntan
- Sunburn (First-Degree Burns)
- Sunburn (Second Degree)
- Wrinkles
- Uneven skin tone
- Freckles
- Melasma (Pregnancy Mask)
- Age Spots (Solar Lentigines)
- Actinic Keratosis (Solar Keratosis)
- Actinic Cheilitis (Farmer’s Lip)
- Squamous Cell Carcinoma
- Bowen Disease
- Basal Cell Carcinoma
- Melanoma
- Cataract
- References

1. Suntan
A tan may look nice, but that golden color is due to an injury to the top layer of your skin.
When you soak up the sun's ultraviolet (UV) rays, it speeds up the aging of your skin and raises your risk of skin cancer.
To prevent damage, use a "broad spectrum" sunscreen that is SPF 30 or higher.

2. Sunburn (First-Degree Burns)
There's no guesswork about whether you've got sunburn. Your skin turns red, it feels hot to the touch, and you may have some mild pain.
It's called a first-degree burn when it affects only the outer layer of your skin. To get some relief from pain, take aspirin or ibuprofen. Try a cold compress, or apply some moisturizing cream or aloe.
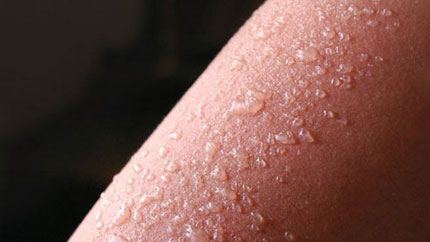
3. Sunburn (Second Degree)
Second-degree sunburn damages deep layers of your skin and nerve endings. It's usually more painful and takes longer to heal.
You may have redness and swelling. Don’t break blisters form. Because they might get infected.

4. Wrinkles
The sun's rays can make you look old. Ultraviolet light in daylight damages the fibers in your skin called elastin. When that happens, it begins to sag and stretch.

5. Uneven skin tone
Too much sun causes some areas of your skin to appear darker, while others look lighter. It can also make permanent changes in small blood vessels, which gives you a reddish look in places.
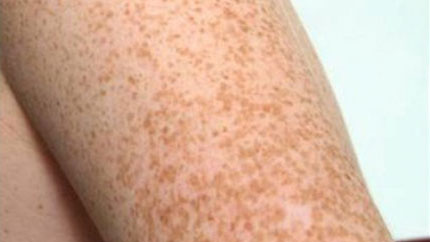
6. Freckles
You get these on areas of your body that are exposed to the sun. You'll notice them more in the summer, especially if you're fair-skinned or have light or red hair.
Freckles aren't bad for you. But some cancers in the earliest stages can look like one.
See your doctor if the size, shape, or color of a spot changes, or if it itches or bleeds.
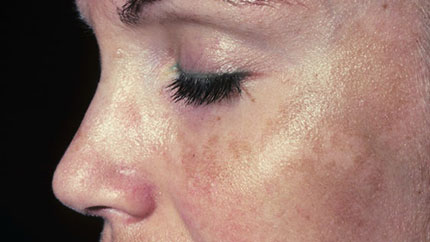
7. Melasma (Pregnancy Mask)
This shows up as tan or brown patches on your cheeks, nose, forehead, and chin. It's common among women who are pregnant, but men can get it too.
It may go away after your pregnancy ends, but you can also treat it with prescription creams and over-the-counter products.
Use sunscreen at all times if you have melasma, because daylight can make it worse.
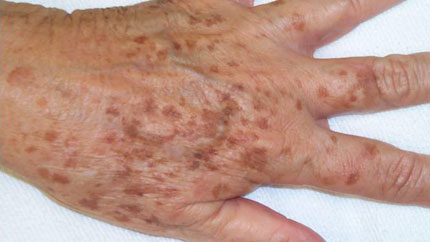
8. Age Spots (Solar Lentigines)
These pesky brown or gray areas aren't really caused by aging, though more of them show up on your body as you get older. You get them from being out in the daylight. They often appear on your face, hands, and chest.
Bleaching creams, acid peels, Retin-A products, and light treatments can make them less obvious. They don't harm your health, but check with your doctor to make sure they're not something more serious, like skin cancer.
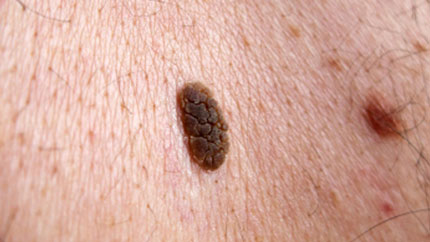
9. Actinic Keratosis (Solar Keratosis)
These red, brown, or skin-colored patches are small and scaly. You get them from being out in the daylight too much. They usually show up on your head, neck, or hands, but they can also appear on other parts of your body.
See your doctor, because if they're not treated they can sometimes turn into squamous cell carcinoma, a type of skin cancer.
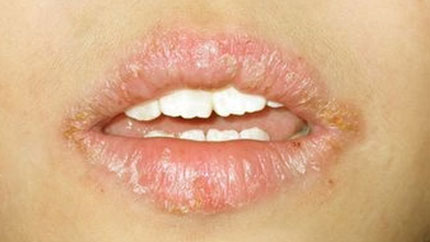
10. Actinic Cheilitis (Farmer’s Lip)
This usually appears on the lower lip, and you may have scaly patches, dryness and cracking, or swelling.
The sharp border-line between your lip and skin may also disappear.
Get this checked by your doctor. It may turn into squamous cell carcinoma if it's not treated.

11. Squamous Cell Carcinoma
This type of skin cancer may show up as a firm red bump, a scaly growth that bleeds or gets a crust, or a sore that doesn't heal. It most often happens on your nose, forehead, ears, lower lip, hands, and other areas that get a lot of sun.
Squamous cell carcinoma can be cured if you get treated early.
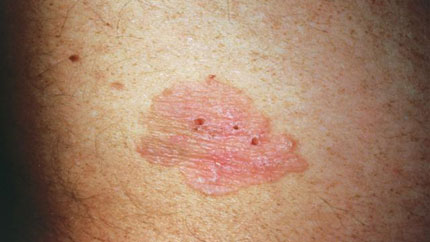
12. Bowen Disease
This is a type of skin cancer that's on the surface of your skin. Your doctor may also call it squamous cell carcinoma "in situ."
Unlike "invasive" squamous cell carcinoma, Bowen disease doesn't spread to the inside of your body. It looks like scaly, reddish patches that may be crusted.

13. Basal Cell Carcinoma
This is the most common form of skin cancer, and it's the easiest to treat.
Basal cell carcinoma spreads slowly. The tumors can take on many forms, including a pearly white or waxy bump, often with visible blood vessels, on the ears, neck, or face.
A tumor can also appear as a flat, scaly, flesh-colored or brown patch on your back or chest, or more rarely, a white, waxy scar.
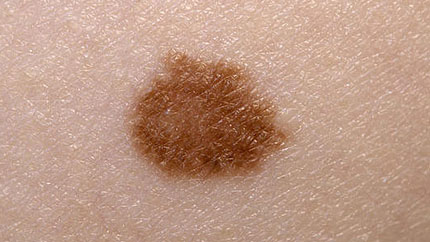
14. Melanoma
It's not as common as other types of skin cancer, but it's the most serious. Possible signs include a change in the way a mole or colored area looks.
Melanoma can affect the skin only, or it may spread to organs and bones. It can be cured if you get early treatment.
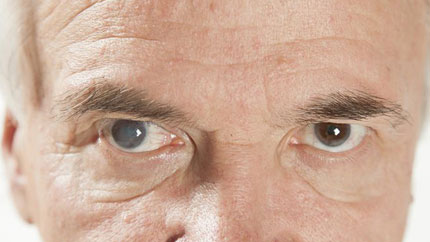
15. Cataract
This is a cloudy area in the lens of your eye. It's painless, but it may cause foggy vision, glare from light, and seeing double. You can help prevent cataracts by wearing a hat and sunglasses when you're in the sun.
